Duodenal Atresia. Duodenal atresia is one of the most common inborn defects of the intestine that is often associated with other congenital malformations and genetic pathologies, e.g. Duodenal atresia can be defined as a congenital problem, in which a part of the duodenum lumen is absent or completely closed. Duodenal atresia is an embryopathy of the cranial intestine that leads to a complete absence of the the incidence of duodenal atresia is between 1/10,000 and 1/6,000 live births, with an approximately. Duodenal atresia results from a congenital malformation of the duodenum and requires prompt correction in the neonatal period. Duodenal atresia is a complete occlusion or absence of the duodenal lumen, whereas duodenal stenosis refers to an incomplete obstruction caused by narrowing. It is thought to be the result of an error in bowel canalisation. The atresia obstructs near the ampulla of vater and. Also known as duodenojejunal atresia. Duodenal atresia means that there is a blockage between one part of the duodenum to another. Duodenal atresia is the most common cause of proximal bowel obstruction in the neonate. It is not open and cannot allow the passage of stomach contents. Often, duodenal atresia is seen on ultrasound performed on a pregnant mother to check on her baby. Duodenal atresia and duodenal stenosis are abnormalities in which there is an absence or complete closure (atresia) in the first part of the small intestines (duodenum) or narrowing (stenosis). Duodenal atresia can be an isolated condition (which means no other birth defect or condition occurs with it), but is also more common in infants with down syndrome (trisomy 21). Duodenal atresia is a condition in which the first part of the small bowel (the duodenum) has not developed properly.
Duodenal Atresia . Fetal Abnormalities » Gastrointestinal Tract.
A Case Of Duodenal Atresia With Apple Peel Appearance Challenging The Current Embryology Pathak M Narula D J Clin Neonatol. Duodenal atresia results from a congenital malformation of the duodenum and requires prompt correction in the neonatal period. Duodenal atresia is a complete occlusion or absence of the duodenal lumen, whereas duodenal stenosis refers to an incomplete obstruction caused by narrowing. Duodenal atresia and duodenal stenosis are abnormalities in which there is an absence or complete closure (atresia) in the first part of the small intestines (duodenum) or narrowing (stenosis). Duodenal atresia is a condition in which the first part of the small bowel (the duodenum) has not developed properly. Duodenal atresia is an embryopathy of the cranial intestine that leads to a complete absence of the the incidence of duodenal atresia is between 1/10,000 and 1/6,000 live births, with an approximately. Duodenal atresia is the most common cause of proximal bowel obstruction in the neonate. Duodenal atresia can be an isolated condition (which means no other birth defect or condition occurs with it), but is also more common in infants with down syndrome (trisomy 21). Duodenal atresia means that there is a blockage between one part of the duodenum to another. Often, duodenal atresia is seen on ultrasound performed on a pregnant mother to check on her baby. Also known as duodenojejunal atresia. Duodenal atresia can be defined as a congenital problem, in which a part of the duodenum lumen is absent or completely closed. The atresia obstructs near the ampulla of vater and. Duodenal atresia is one of the most common inborn defects of the intestine that is often associated with other congenital malformations and genetic pathologies, e.g. It is not open and cannot allow the passage of stomach contents. It is thought to be the result of an error in bowel canalisation.
It receives contents emptied from the stomach.
Duodenal atresia is the most common cause of proximal bowel obstruction in the neonate. Duodenal atresia means that there is a blockage between one part of the duodenum to another. Fetal abnormalities » gastrointestinal tract. 74 duodenal atresia is the congenital absence or complete closure of a portion of the. Often, duodenal atresia is seen on ultrasound performed on a pregnant mother to check on her baby. Duodenal atresia information including symptoms, diagnosis, misdiagnosis, treatment, causes duodenal atresia: In duodenal atresia the duodenum fails to canalize properly late in the first trimester and a web or several webs occur. Duodenal atresia can be an isolated condition (which means no other birth defect or condition occurs with it), but is also more common in infants with down syndrome (trisomy 21). Duodenal atresia, midgut malrotation and volvulus, jejunoileal atresia, meconium ileus and necrotizing enterocolitis are the most common causes of neonatal intestinal obstruction. Duodenal atresia is a condition in which the first part of the small bowel (the duodenum) has not developed properly. Duodenal atresia, also known as duodenal stenosis, is related to wikipedia : The duodenum is the first portion of the small intestine that receives contents emptied from the stomach. Also known as duodenojejunal atresia. Duodenal atresia has been reported in association with various malformations and syndromes common being down syndrome, malrotation, and annular pancreas. Duodenal atresia is one of the most common inborn defects of the intestine that is often associated with other congenital malformations and genetic pathologies, e.g. Duodenal atresia occurs in one out of every 2,500 live births. Reassessment of treatment and outcome based on antenatal fonkalsrud ew. Duodenal atresia is one of the more common congenital intestinal anomalies.… duodenal atresia (duodenum atresia): Duodenal atresia is the most common cause of proximal bowel obstruction in the neonate. Here another case of duodenal atresia with the typical double bubble sign. Read more about symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, complications. 'double bubble' sign as a result of an enlarged stomach and duodenal cap. Duodenal atresia is a condition in which the first part of the small bowel (the duodenum) has not developed properly. Duodenal atresia is a complete occlusion or absence of the duodenal lumen, whereas duodenal stenosis refers to an incomplete obstruction caused by narrowing. It is thought to be the result of an error in bowel canalisation. This is the first portion of the small intestine; Below is the list of complications and problems that may arise if duodenal atresia is left untreated Duodenal atresia (also called duodenal stenosis) is a rare congenital (present at birth) disorder of the duodenum. Duodenal atresia and duodenal stenosis are abnormalities in which there is an absence or complete closure (atresia) in the first part of the small intestines (duodenum) or narrowing (stenosis). Duodenal atresia, unlike other intestinal atresias, is commonly associated with other congenital anomalies such as down syndrome, which is present in 25 to 40% of cases. It is not open and cannot allow the passage of stomach contents.
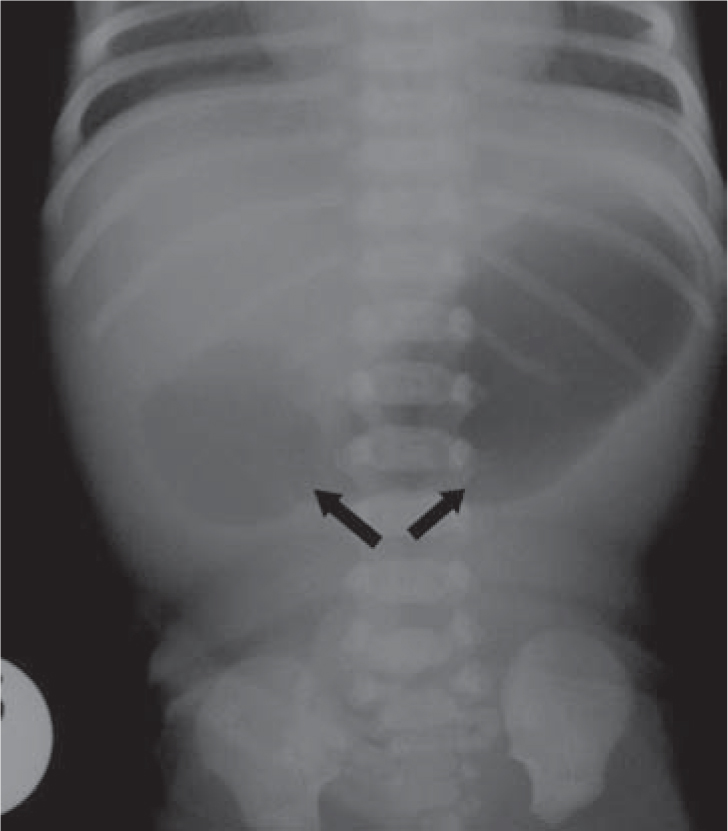
Duodenal Atresia . 'Double Bubble' Sign As A Result Of An Enlarged Stomach And Duodenal Cap.
Esophageal Atresia Duodenal Atresia And Imperforate Anus Triple Atresia Panda Ss Srinivas M Bajpai M Sharma N Singh A Baidya Dk Jana M J Clin Neonatol. Duodenal atresia results from a congenital malformation of the duodenum and requires prompt correction in the neonatal period. The atresia obstructs near the ampulla of vater and. Duodenal atresia is a complete occlusion or absence of the duodenal lumen, whereas duodenal stenosis refers to an incomplete obstruction caused by narrowing. Often, duodenal atresia is seen on ultrasound performed on a pregnant mother to check on her baby. Duodenal atresia is one of the most common inborn defects of the intestine that is often associated with other congenital malformations and genetic pathologies, e.g. Duodenal atresia is an embryopathy of the cranial intestine that leads to a complete absence of the the incidence of duodenal atresia is between 1/10,000 and 1/6,000 live births, with an approximately. It is not open and cannot allow the passage of stomach contents. Duodenal atresia can be an isolated condition (which means no other birth defect or condition occurs with it), but is also more common in infants with down syndrome (trisomy 21). Duodenal atresia and duodenal stenosis are abnormalities in which there is an absence or complete closure (atresia) in the first part of the small intestines (duodenum) or narrowing (stenosis). Duodenal atresia is a condition in which the first part of the small bowel (the duodenum) has not developed properly. Duodenal atresia is the most common cause of proximal bowel obstruction in the neonate. Duodenal atresia means that there is a blockage between one part of the duodenum to another. It is thought to be the result of an error in bowel canalisation. Also known as duodenojejunal atresia. Duodenal atresia can be defined as a congenital problem, in which a part of the duodenum lumen is absent or completely closed.
Fetal Duodenum , Duodenal Atresia Can Be An Isolated Condition (Which Means No Other Birth Defect Or Condition Occurs With It), But Is Also More Common In Infants With Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21).
Duodenal Atresia. It is not open and cannot allow the passage of stomach contents. Duodenal atresia results from a congenital malformation of the duodenum and requires prompt correction in the neonatal period. Also known as duodenojejunal atresia. Duodenal atresia can be an isolated condition (which means no other birth defect or condition occurs with it), but is also more common in infants with down syndrome (trisomy 21). Duodenal atresia is a condition in which the first part of the small bowel (the duodenum) has not developed properly. It is thought to be the result of an error in bowel canalisation. The atresia obstructs near the ampulla of vater and. Duodenal atresia is one of the most common inborn defects of the intestine that is often associated with other congenital malformations and genetic pathologies, e.g. Often, duodenal atresia is seen on ultrasound performed on a pregnant mother to check on her baby. Duodenal atresia is an embryopathy of the cranial intestine that leads to a complete absence of the the incidence of duodenal atresia is between 1/10,000 and 1/6,000 live births, with an approximately.
Duodenal Atresia Duodenal Obstruction Medlife Institute Of Ultrasonography Facebook . Duodenal atresia is an embryopathy of the cranial intestine that leads to a complete absence of the approximately 20 to 30% of infants with duodenal atresia are carriers of trisomy 21, and about 20 to.
Frontiers The Role Of Fibroblast Growth Factor 10 Signaling In Duodenal Atresia Pharmacology. Duodenal atresia is one of the most common inborn defects of the intestine that is often associated with other congenital malformations and genetic pathologies, e.g. Duodenal atresia is an embryopathy of the cranial intestine that leads to a complete absence of the the incidence of duodenal atresia is between 1/10,000 and 1/6,000 live births, with an approximately. Duodenal atresia is a complete occlusion or absence of the duodenal lumen, whereas duodenal stenosis refers to an incomplete obstruction caused by narrowing. It is not open and cannot allow the passage of stomach contents. It is thought to be the result of an error in bowel canalisation. Duodenal atresia can be an isolated condition (which means no other birth defect or condition occurs with it), but is also more common in infants with down syndrome (trisomy 21). The atresia obstructs near the ampulla of vater and. Duodenal atresia can be defined as a congenital problem, in which a part of the duodenum lumen is absent or completely closed. Duodenal atresia is the most common cause of proximal bowel obstruction in the neonate. Often, duodenal atresia is seen on ultrasound performed on a pregnant mother to check on her baby. Also known as duodenojejunal atresia. Duodenal atresia results from a congenital malformation of the duodenum and requires prompt correction in the neonatal period. Duodenal atresia is a condition in which the first part of the small bowel (the duodenum) has not developed properly. Duodenal atresia and duodenal stenosis are abnormalities in which there is an absence or complete closure (atresia) in the first part of the small intestines (duodenum) or narrowing (stenosis). Duodenal atresia means that there is a blockage between one part of the duodenum to another.
Cxr Kub Showing Double Bubble Sign Of Duodenal Atresia Elevated Left Download Scientific Diagram , Duodenal Atresia And Duodenal Stenosis Are Abnormalities In Which There Is An Absence Or Complete Closure (Atresia) In The First Part Of The Small Intestines (Duodenum) Or Narrowing (Stenosis).
Duodenal Atresia Mnemonic Youtube. The atresia obstructs near the ampulla of vater and. Duodenal atresia can be defined as a congenital problem, in which a part of the duodenum lumen is absent or completely closed. Duodenal atresia is a complete occlusion or absence of the duodenal lumen, whereas duodenal stenosis refers to an incomplete obstruction caused by narrowing. Duodenal atresia results from a congenital malformation of the duodenum and requires prompt correction in the neonatal period. It is not open and cannot allow the passage of stomach contents. Duodenal atresia can be an isolated condition (which means no other birth defect or condition occurs with it), but is also more common in infants with down syndrome (trisomy 21). Duodenal atresia is one of the most common inborn defects of the intestine that is often associated with other congenital malformations and genetic pathologies, e.g. Duodenal atresia is an embryopathy of the cranial intestine that leads to a complete absence of the the incidence of duodenal atresia is between 1/10,000 and 1/6,000 live births, with an approximately. It is thought to be the result of an error in bowel canalisation. Duodenal atresia is a condition in which the first part of the small bowel (the duodenum) has not developed properly. Duodenal atresia means that there is a blockage between one part of the duodenum to another. Duodenal atresia is the most common cause of proximal bowel obstruction in the neonate. Also known as duodenojejunal atresia. Duodenal atresia and duodenal stenosis are abnormalities in which there is an absence or complete closure (atresia) in the first part of the small intestines (duodenum) or narrowing (stenosis). Often, duodenal atresia is seen on ultrasound performed on a pregnant mother to check on her baby.
Learning About Duodenal Atresia Repair In Children . Duodenal Atresia Can Be Defined As A Congenital Problem, In Which A Part Of The Duodenum Lumen Is Absent Or Completely Closed.
Duodenal Atresia. Duodenal atresia is the most common cause of proximal bowel obstruction in the neonate. It is not open and cannot allow the passage of stomach contents. Duodenal atresia is a condition in which the first part of the small bowel (the duodenum) has not developed properly. Duodenal atresia is a complete occlusion or absence of the duodenal lumen, whereas duodenal stenosis refers to an incomplete obstruction caused by narrowing. Duodenal atresia is one of the most common inborn defects of the intestine that is often associated with other congenital malformations and genetic pathologies, e.g. Duodenal atresia can be defined as a congenital problem, in which a part of the duodenum lumen is absent or completely closed. Often, duodenal atresia is seen on ultrasound performed on a pregnant mother to check on her baby. It is thought to be the result of an error in bowel canalisation. Duodenal atresia results from a congenital malformation of the duodenum and requires prompt correction in the neonatal period. The atresia obstructs near the ampulla of vater and. Also known as duodenojejunal atresia. Duodenal atresia means that there is a blockage between one part of the duodenum to another. Duodenal atresia is an embryopathy of the cranial intestine that leads to a complete absence of the the incidence of duodenal atresia is between 1/10,000 and 1/6,000 live births, with an approximately. Duodenal atresia and duodenal stenosis are abnormalities in which there is an absence or complete closure (atresia) in the first part of the small intestines (duodenum) or narrowing (stenosis). Duodenal atresia can be an isolated condition (which means no other birth defect or condition occurs with it), but is also more common in infants with down syndrome (trisomy 21).
Duodenal Atresia In Newborns With Abnormality On Prenatal Ultrasound Download Scientific Diagram , Duodenal Atresia Is The Most Common Cause Of Proximal Bowel Obstruction In The Neonate.
Duodenal Atresia Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org. It is not open and cannot allow the passage of stomach contents. Duodenal atresia is a condition in which the first part of the small bowel (the duodenum) has not developed properly. Duodenal atresia and duodenal stenosis are abnormalities in which there is an absence or complete closure (atresia) in the first part of the small intestines (duodenum) or narrowing (stenosis). Duodenal atresia is the most common cause of proximal bowel obstruction in the neonate. Duodenal atresia is a complete occlusion or absence of the duodenal lumen, whereas duodenal stenosis refers to an incomplete obstruction caused by narrowing. The atresia obstructs near the ampulla of vater and. Duodenal atresia is one of the most common inborn defects of the intestine that is often associated with other congenital malformations and genetic pathologies, e.g. Often, duodenal atresia is seen on ultrasound performed on a pregnant mother to check on her baby. Duodenal atresia is an embryopathy of the cranial intestine that leads to a complete absence of the the incidence of duodenal atresia is between 1/10,000 and 1/6,000 live births, with an approximately. It is thought to be the result of an error in bowel canalisation. Duodenal atresia can be an isolated condition (which means no other birth defect or condition occurs with it), but is also more common in infants with down syndrome (trisomy 21). Also known as duodenojejunal atresia. Duodenal atresia can be defined as a congenital problem, in which a part of the duodenum lumen is absent or completely closed. Duodenal atresia means that there is a blockage between one part of the duodenum to another. Duodenal atresia results from a congenital malformation of the duodenum and requires prompt correction in the neonatal period.
Duodenal Atresia - Duodenal Atresia Is An Embryopathy Of The Cranial Intestine That Leads To A Complete Absence Of The Approximately 20 To 30% Of Infants With Duodenal Atresia Are Carriers Of Trisomy 21, And About 20 To.
Learn About A Condition American Pediatric Surgical Association. Duodenal atresia is a complete occlusion or absence of the duodenal lumen, whereas duodenal stenosis refers to an incomplete obstruction caused by narrowing. Duodenal atresia and duodenal stenosis are abnormalities in which there is an absence or complete closure (atresia) in the first part of the small intestines (duodenum) or narrowing (stenosis). Duodenal atresia is one of the most common inborn defects of the intestine that is often associated with other congenital malformations and genetic pathologies, e.g. Duodenal atresia can be an isolated condition (which means no other birth defect or condition occurs with it), but is also more common in infants with down syndrome (trisomy 21). Duodenal atresia is an embryopathy of the cranial intestine that leads to a complete absence of the the incidence of duodenal atresia is between 1/10,000 and 1/6,000 live births, with an approximately. Duodenal atresia means that there is a blockage between one part of the duodenum to another. The atresia obstructs near the ampulla of vater and. Duodenal atresia is a condition in which the first part of the small bowel (the duodenum) has not developed properly. It is thought to be the result of an error in bowel canalisation. It is not open and cannot allow the passage of stomach contents. Duodenal atresia can be defined as a congenital problem, in which a part of the duodenum lumen is absent or completely closed. Duodenal atresia results from a congenital malformation of the duodenum and requires prompt correction in the neonatal period. Also known as duodenojejunal atresia. Duodenal atresia is the most common cause of proximal bowel obstruction in the neonate. Often, duodenal atresia is seen on ultrasound performed on a pregnant mother to check on her baby.
Fetal Mri Duodenal Atresia . 'Double Bubble' Sign As A Result Of An Enlarged Stomach And Duodenal Cap.
Congenital And Neonatal Abnormalities Radiology Key. Also known as duodenojejunal atresia. Duodenal atresia results from a congenital malformation of the duodenum and requires prompt correction in the neonatal period. Duodenal atresia and duodenal stenosis are abnormalities in which there is an absence or complete closure (atresia) in the first part of the small intestines (duodenum) or narrowing (stenosis). Duodenal atresia means that there is a blockage between one part of the duodenum to another. It is thought to be the result of an error in bowel canalisation. Often, duodenal atresia is seen on ultrasound performed on a pregnant mother to check on her baby. Duodenal atresia is the most common cause of proximal bowel obstruction in the neonate. Duodenal atresia is an embryopathy of the cranial intestine that leads to a complete absence of the the incidence of duodenal atresia is between 1/10,000 and 1/6,000 live births, with an approximately. The atresia obstructs near the ampulla of vater and. Duodenal atresia is a complete occlusion or absence of the duodenal lumen, whereas duodenal stenosis refers to an incomplete obstruction caused by narrowing. It is not open and cannot allow the passage of stomach contents. Duodenal atresia can be defined as a congenital problem, in which a part of the duodenum lumen is absent or completely closed. Duodenal atresia can be an isolated condition (which means no other birth defect or condition occurs with it), but is also more common in infants with down syndrome (trisomy 21). Duodenal atresia is one of the most common inborn defects of the intestine that is often associated with other congenital malformations and genetic pathologies, e.g. Duodenal atresia is a condition in which the first part of the small bowel (the duodenum) has not developed properly.
Duodenal Atresia Congenital Disorder Surgery : Duodenal Atresia Has Been Reported In Association With Various Malformations And Syndromes Common Being Down Syndrome, Malrotation, And Annular Pancreas.
Epos Trade. Duodenal atresia can be defined as a congenital problem, in which a part of the duodenum lumen is absent or completely closed. Duodenal atresia is an embryopathy of the cranial intestine that leads to a complete absence of the the incidence of duodenal atresia is between 1/10,000 and 1/6,000 live births, with an approximately. Duodenal atresia can be an isolated condition (which means no other birth defect or condition occurs with it), but is also more common in infants with down syndrome (trisomy 21). Often, duodenal atresia is seen on ultrasound performed on a pregnant mother to check on her baby. It is thought to be the result of an error in bowel canalisation. Also known as duodenojejunal atresia. Duodenal atresia is a condition in which the first part of the small bowel (the duodenum) has not developed properly. Duodenal atresia means that there is a blockage between one part of the duodenum to another. Duodenal atresia is one of the most common inborn defects of the intestine that is often associated with other congenital malformations and genetic pathologies, e.g. Duodenal atresia is the most common cause of proximal bowel obstruction in the neonate. The atresia obstructs near the ampulla of vater and. It is not open and cannot allow the passage of stomach contents. Duodenal atresia results from a congenital malformation of the duodenum and requires prompt correction in the neonatal period. Duodenal atresia and duodenal stenosis are abnormalities in which there is an absence or complete closure (atresia) in the first part of the small intestines (duodenum) or narrowing (stenosis). Duodenal atresia is a complete occlusion or absence of the duodenal lumen, whereas duodenal stenosis refers to an incomplete obstruction caused by narrowing.
Duodenal Atresia Symptoms In Kids Children S Minnesota - In Duodenal Atresia The Duodenum Fails To Canalize Properly Late In The First Trimester And A Web Or Several Webs Occur.
Medpix Case Duodenal Atresia. Duodenal atresia results from a congenital malformation of the duodenum and requires prompt correction in the neonatal period. Duodenal atresia can be an isolated condition (which means no other birth defect or condition occurs with it), but is also more common in infants with down syndrome (trisomy 21). Duodenal atresia can be defined as a congenital problem, in which a part of the duodenum lumen is absent or completely closed. Often, duodenal atresia is seen on ultrasound performed on a pregnant mother to check on her baby. It is thought to be the result of an error in bowel canalisation. Duodenal atresia is one of the most common inborn defects of the intestine that is often associated with other congenital malformations and genetic pathologies, e.g. The atresia obstructs near the ampulla of vater and. Duodenal atresia is an embryopathy of the cranial intestine that leads to a complete absence of the the incidence of duodenal atresia is between 1/10,000 and 1/6,000 live births, with an approximately. Duodenal atresia means that there is a blockage between one part of the duodenum to another. Duodenal atresia is the most common cause of proximal bowel obstruction in the neonate. Duodenal atresia is a condition in which the first part of the small bowel (the duodenum) has not developed properly. Duodenal atresia is a complete occlusion or absence of the duodenal lumen, whereas duodenal stenosis refers to an incomplete obstruction caused by narrowing. Also known as duodenojejunal atresia. It is not open and cannot allow the passage of stomach contents. Duodenal atresia and duodenal stenosis are abnormalities in which there is an absence or complete closure (atresia) in the first part of the small intestines (duodenum) or narrowing (stenosis).